Azure offers a few different integration messaging services. Each Azure service is designed for a particular integration scenario to support modern architectural trends like microservices and event-driven architecture.
Let’s highlight each azure messaging service’s unique characteristics and choose the right services based on your different integration scenarios. We will focus on basic features like Ordering guarantees, pull and push models and the minimum cost per 10 million operations per month of each service.
Message Vs. Event
Messaging services are intended to have clear intent and are sent for specific action or response. For instance, when a message is sent to the warehouse service, request a product to be prepared for a pickup after a customer placed an order. This message is intended for a command that requires action and expects to receive an acknowledgment from the received services. On the other hand, Events are also messages, but they don’t generally convey a publisher intent other than to inform. An event captures a fact and conveys that fact. A consumer of the event can process the facts as they please and doesn’t fulfill any publisher’s specific expectations.
Azure service broker services could be grouped into two main groups: the messaging-based group like Service bus and Storage Queue, and event-based groups like Event hub and Event Grid.
Azure Messaging Services
Azure service bus and storage queues are messaging mechanisms that store all received messages from publisher services in a queue, waiting for consumers’ services to consume these messages.
Azure Service Bus
Cost & Tiers
- The Service Bus is offered in three different tiers Basic, Standard and Dedicated
- Minimum cost of 10 million operations per month for each tier based on the 2021 azure calculator
- Basic: $11.23
- Standards: $22.18
- Dedicated: $6,260.48
Main Features
The Azure service bus We recommend considering if the integration service requires the following features:
- Ordering support by guaranteeing delivery of messages in orders like FIFO (First-in, First-out) requires a standard tier or higher.
- It supports the pulling mechanism only; this could be required if the service is not available all the time or has low processing capabilities.
- Push mechanisms are not supported unless you will be using the Dedicated tier.
- Other advanced features like batching/sessions, transactions, dead-lettering, temporal control, routing and filtering, and duplicate detection
Azure storage queue
Cost
- Offered as part of Azure storage service.
- The minimum cost of 10 million operations and 100 GB of storage per month is $8.90 (Azure Storage Pricing, 2021)
Main Features
- Supports the pulling mechanism only
- Storage queue doesn’t guarantee message delivery ordering
- Able to store over 80 gigabytes of messages in a queue.
Storage queues are mainly recommended for basic services, which require basic queuing features without the need for advanced features of azure service bus like order guarantees and support of high traffic of messages.
Azure Event Services
Event Hub
Event Hub is an events-based service intended to be used as a big data pipeline with very low latency and can receive and process millions of events per second.
Cost & Tiers
- Offered in three tier Basic, Standard and Dedicated
- Minimum cost of 10 million operations per month for each tier (Microsoft, 2021)
- Basic: $ 11.23
- Standards: $ 22.18
- Dedicated: $ 4,999.77
- The minimum cost for data capturing feature is about $100 per month
Main Features
- Support ordering by guaranteeing delivery of messages on orders like FIFO (First-in, First-out) and supported by basic tier
- It supports both polling and pushing mechanisms; however, it’s the service’s responsibility to keep track of the received events by storing the offset number of the last received event.
- You can capture the streaming data into a file for processing and analysis.
- Enable rapid data retrieval for real-time processing as well as a repeated replay of stored raw data
Event Grid
Event Grid enables event-driven, reactive programming. It uses a publish-subscribe model and events to be pushed to subscribers as soon as it happens.
Cost
- The event grid doesn’t have different tiers, but the minimum cost for 10 operations per month is about $8.16
Main Features
- No support for event ordering or pulling mechanism
- Supports pushing mechanism
- guaranteeing at least once delivery
- Event Grid supports dead-lettering for events that aren’t delivered to an endpoint
- Provides out of the box integration with various Azure services like Azure Functions and Logic Apps
- Event Grid isn’t a data pipeline and doesn’t deliver the actual data object that was updated.
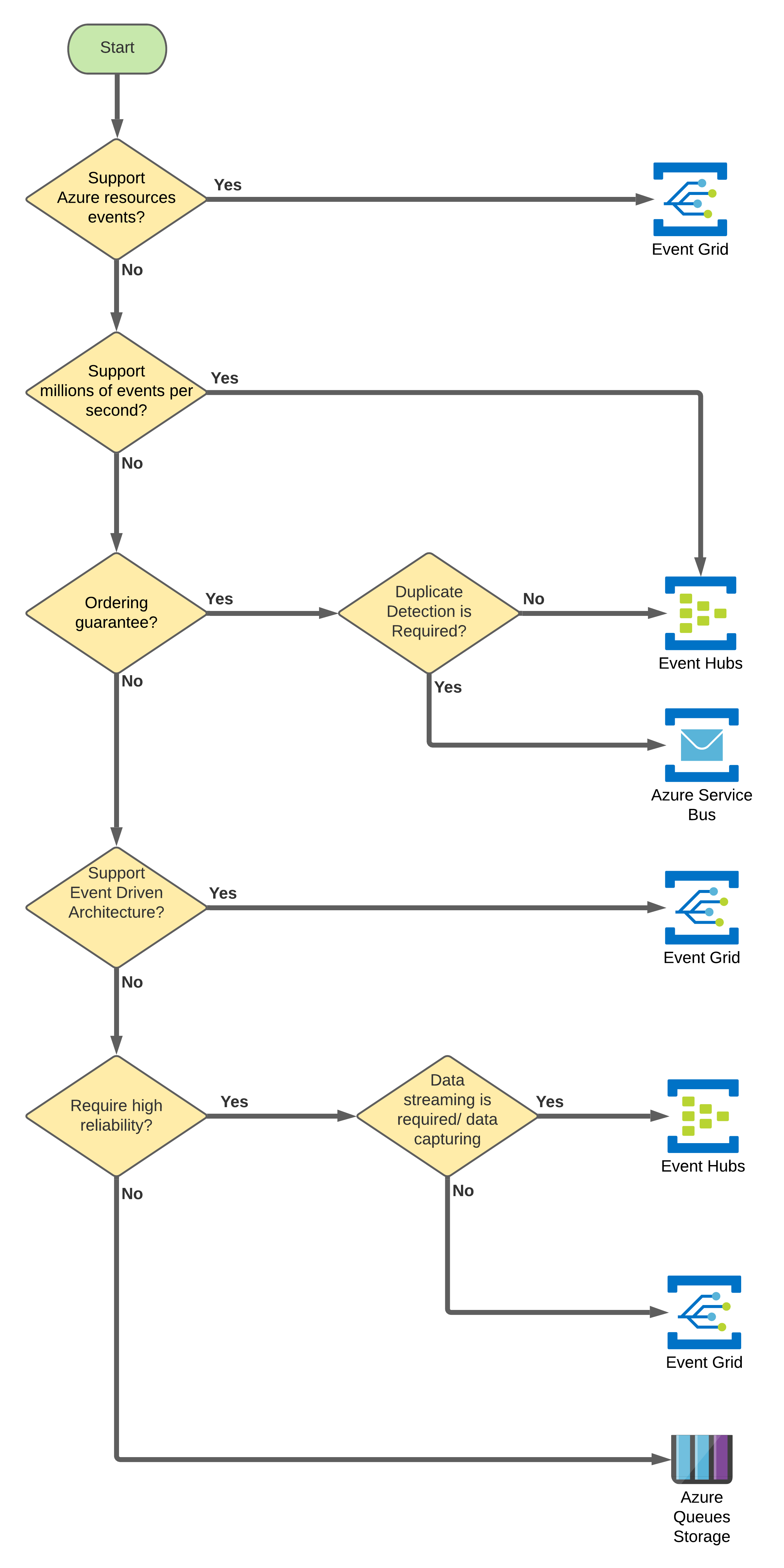
Are you still lost?
You can follow the decision workflow diagram below if you are still lost on which service you should be using for your integration project.

Final Thought
It will be hard to draw sharp lines between the various use cases of each service. So, the system architect could mix between different services to get the best value of each service. For example, the event hub could emit events to the Event grid to process the event. Azure service brokers don’t force system architecture into hard decisions when choosing between services, and it’s common for a single system to use different service brokers.

Leave a Reply